Key Components of the 1st Framework on Marine debris Management(2021~2030)
Key Components of the 1st Framework on Marine debris Management (2021~2030)
Achieve 60% Reduction in Marine Plastic Debris inflow by 2030, Zero by 2050
In May 2021, the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries announced the establishment of the 1st Framework on Marine Debris Management(2021~2030) which conveys systematic policies on marine debris management and implementation projects for the next decade.
Marine debris has so far been managed under the principle of 「Marine Environment Management Act」, mainly dealt with its collection and disposal. Accordingly, the conventional mechanism of marine debris management failed to establish a stable management system as well as reduce the total volume of debris. In this regard, the government aims to build an exclusive management system via enacting and implementing 「Management Act on Marine debris and Pollutant」in December 2020 along with the establishment of the 1st framework.
The framework consists of 5 main strategies for implementation as well as 16 projects for implementation under the goal of enhancing the life cycle of marine debris production, collection and disposal, along with the strengthened partnerships with relevant authorities. The framework aims to reduce 60% of the total marine plastics debris inflow by 2030 and to achieve zero by 2050.
Strategy 1. Prevention
The first strategy is prevention, which introduces the deposit system* on buoy and fishing gear to prevent the fundamental cause of debris production, expands the distributing scope of eco-friendly buoy, blocks the influx of land debris to the oceans and establishes the preventive mechanism against overseas marine debris via engaging in international organizations and bilateral partnerships.
*Expand the use of eco-friendly fishing gears that are easy to detach from fishing boats, under the introduction of the deposit system (fish trap in 2022→gill net in 2025) and expanded use of eco-friendly buoy(‘21 39%→ ’22 59% → ‘24 100%).
** Gradual introduction and implementation of the comprehensive management of the total volume of river debris.
- (Phase 1) estimate the amount of flow-in river debris(5 main rivers) to the oceans to bring more effectiveness on management.
- (Phase 2) estimate the possible reduction percentage of the 5 main rivers with mid, long-term goals.
- (Phase 3) establish and operate a multilateral working group among MOF, MOE and local governments to effectively manage the river debris, along with the 1st pilot program.
- ※ Firstly conduct the monitoring project after discussing with relevant ministries(MOE)
Strategy 2. Improved System on Collection·Delivery
In order to prevent blind spot of debris collection, the Ministry aims to deploy 7 cleaning vessels in the island areass(~‘22), secure enough drop-off stations for collected marine debris(‘20: 30 → ’30: 300 stations), implement responsive mechanism against the massive influx of debris due to natural disasters such as typhoon and floods. With that said, MOF also operates consultative groups with relevant authorities for joint debris collection and improves the overall collecting mechanism.
* Preventive measures shall take place as groups are deployed at the beaches on a regular basis.
On top of that, a forecast system shall be developed to predict production and flow of marine debris based on the active utilization of ICT, artificial satellite and drone. This will also lead to further enhancement of effective collecting mechanism including relevant equipment in remote areas which lack of accessibility of marine plastics and debris.

Scaled-down cleaning vessel for remote areas

Scaled-down cleaning equipment to collect marine plastic debris
Strategy 3. Encouraging Disposal·Recycling
The management infrastructure shall be expanded and further supported via enhancing the installment of life cycle on marine debris and capacity of relevant agencies. Along with this, an energized system catered to islands and fishing communities shall be developed and distributable models shall be conducted contributing to the establishment of circular economy town.
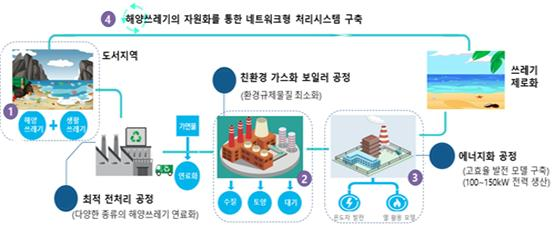
Table of Energized System catered to islands·fishing communities on marine debris management
Strategy 4. Enhancing Management Basis
The Ministry also designates and operates a interministerial committee to handle the life cycle of marine debris at the government level, specializing the managing authority with much enhanced expertise on marine debris management.
Furthermore, regular analysis shall be conducted in order to ease concerns over the impacts caused by micro-plastic debris on marine ecosystem, as well as countermeasures shall be come up with considering all possible impacts and nature of micro-plastics comprehensively.
Strategy 5. Promoting Public Awareness
Joint efforts shall be made among the government, local governments, relevant authorities as well as various public engagement shall take place including Adopt-a-Beach Movement to increase public participation. Meanwhile, educational programs will be developed, distributed and promotional contents will also be implemented for various social brackets such as civilians, fishermen, students.
* Implement cleaning programs among individuals, groups, companies to pick particular beaches.
→ Expand the scope of Adopt-a-Beach starting from Jeju island, Incheon, Gyeongnam, Chungnam in 2021.

